Policies, Recommendations and Joint Statements

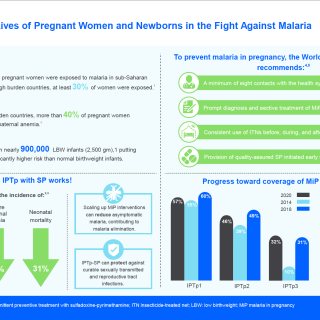
Malaria protection in pregnancy: A lifesaving intervention for preventing neonatal mortality and low birth weight summarizes the evidence of the protective effect of malaria prevention in pregnancy on neonatal mortality. The brief

Joint Statement by the Roll Back Malaria Working Groups on Malaria in Pregnancy and Vector Control and the Alliance for Malaria Prevention, February 2015

MIP Consensus Statement: Optimizing the delivery of malaria-in-pregnancy interventions

Malaria protection in pregnancy: A lifesaving intervention for preventing neonatal mortality and low birth weight summarizes the evidence of the protective effect of malaria prevention in pregnancy on neonatal mortality. The brief

WHO policy brief for the implementation of intermittent preventive treatment of malaria in pregnancy using sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine (IPTp-SP)April 2013

Updated WHO policy recommendation: intermittent preventive treatment of malaria in pregnancy using sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine (IPTp-SP)October 2012

Updated WHO policy recommendation (2016): WHO recommendations on antenatal care for a positive pregnancy experience

WHO: Information note on recommended selection criteria for procurement of malaria rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs)

Determinants of uptake of intermittent preventive treatment during pregnancy: a review (Roman, et. al 2019)
Guidance documents
Implementing Malaria in Pregnancy Programs in the Context of World Health Organization Recommendations on Antenatal Care for a Positive Pregnancy Experience